
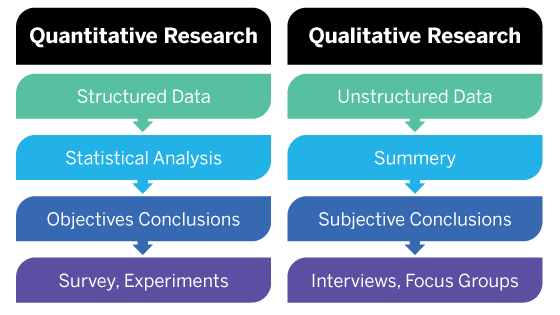

For example, if something weighs 20 kilograms, that can be considered an objective fact. Quantitative data is fixed and “universal,” while qualitative data is subjective and dynamic.Qualitative data can help us to understand the “why” or “how” behind certain behaviors, or it can simply describe a certain attribute-for example, “The postbox is red” or “I signed up to the email newsletter because I’m really interested in hearing about local events.” “20 people signed up to our email newsletter last week”). Quantitative data tells us how many, how much, or how often (e.g.Qualitative data is descriptive, relating to language. Quantitative data is countable or measurable, relating to numbers.Let’s summarize the key differences before exploring each aspect in more detail: The main differences between quantitative and qualitative data lie in what they tell us, how they are collected, and how they are analyzed. What are the main differences between quantitative and qualitative data? Qualitative data also refers to the words or labels used to describe certain characteristics or traits-for example, describing the sky as blue or labeling a particular ice cream flavor as vanilla. In this case, you’re not just looking at numbers you’re asking the user to tell you, using language, why they did something or how they feel. Perhaps you want to know how a user feels about a particular product again, qualitative data can provide such insights. For example, if your quantitative data tells you that a certain website visitor abandoned their shopping cart three times in one week, you’d probably want to investigate why-and this might involve collecting some form of qualitative data from the user.

Researchers will often turn to qualitative data to answer “Why?” or “How?” questions. It’s descriptive, expressed in terms of language rather than numerical values. Unlike quantitative data, qualitative data cannot be measured or counted. Learn more: What is quantitative data? A complete introduction What is qualitative data? To analyze and make sense of quantitative data, you’ll conduct statistical analyses. Quantitative data can tell you “how many,” “how much,” or “how often”-for example, how many people attended last week’s webinar? How much revenue did the company make in 2019? How often does a certain customer group use online banking? If it can be counted or measured, and given a numerical value, it’s quantitative data. Quantitative data refers to any information that can be quantified. Each requires different collection and analysis methods, so it’s important to understand the difference between the two. When it comes to conducting research and data analysis, you’ll work with two types of data: quantitative and qualitative. What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative data? When should I use qualitative or quantitative data?.What are the advantages and disadvantages of quantitative vs qualitative data?.Quantitative vs qualitative data: Methods of analysis.How are quantitative and qualitative data collected?.What are the different types of quantitative and qualitative data?.Quantitative vs qualitative data: What are they, and what’s the difference between them?.Want to skip ahead to a specific section? Just use this clickable menu: We’ll also include useful examples throughout.īy the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the difference between qualitative and quantitative data, and a good idea of when to use which. We’ll then explore all the key ways in which they differ-from how they are collected and analyzed, to the advantages and disadvantages of each. In this post, we’ll define both quantitative and qualitative data in more detail. Qualitative data is descriptive, referring to things that can be observed but not measured-such as colors or emotions. Quantitative data is anything that can be counted or measured it refers to numerical data. If you’re considering a career in data-or in any kind of research field, like psychology-you’ll need to get to grips with two types of data: Quantitative and qualitative.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
